If the Q factor goes lower the energy loss goes higher. Resonant frequency is the natural frequency where a medium vibrates at the highest amplitude.

What Is Sharpness Of Resonance Q Factor Of Rlc Circuit Coil
In doing so damping reduces the maximum amplitude of the vibration at resonance and increases the width of the amplification zone see Figure 2.

. How under-damped an oscillator or resonator will be described by the Q factor. Copy in fluids small biological mass detection via resonant frequency shift and viscometry continues to grow. Resonance is a ubiquitous phenomenon observed in a wide range of physical systems.
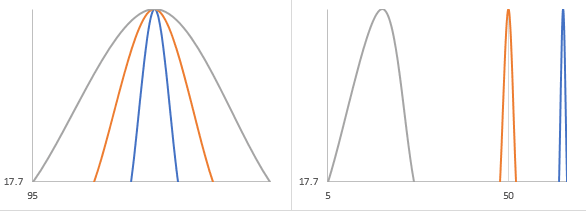
The higher the Q factor the greater the amplitude at the resonant frequency and the smaller the bandwidth or range of frequencies around resonance occurs. The Q factor is used to measure how narrow or broad the band of frequencies are near resonance. Combining several pendulums or springs can lead to even more unexpected motions.
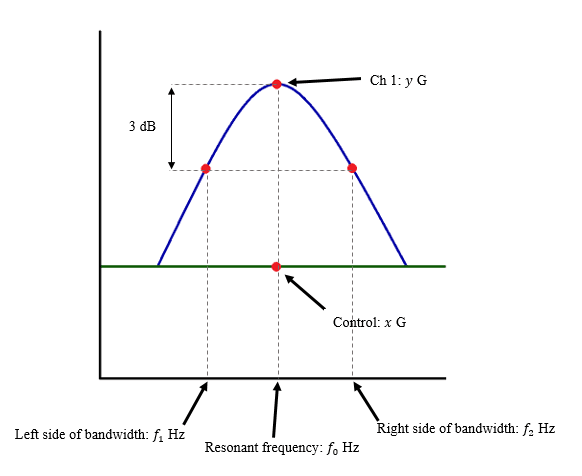
The 0707 current points correspond to the half power points since P I 2 R 0707 2 05. Here we will discuss only parallel-resonance phenomena which are the most frequent. Through algebraic substitution write an equation that gives the Q factor of a series resonant LC circuit exclusively in terms of L C and R without reference to reactance X or frequency f.
Thus far in this unit applications of sound wave principles have been made towards a discussion of beats. Damping absorbs vibratory energy converting it to heat. The last approximation is only valid when Q is larger than 2 or 3.
A large Q also means that the power absorbed or dissipate is also large. In electrical resonance a high- Q circuit in a radio receiver is more difficult to tune but has greater selectivity and so would be better at filtering out signals from other stations. Bandwidth is measured between the 0707 current amplitude points.
We estimate the quality factor Q and resonant frequency f o of a microwave cavity based on resonance curve observations on an equally-spaced frequency grid. Bandwidth Δf is measured between the 707 amplitude points of series. Both types of actuators tend to have a high Q factor which draws a high resonance sharpness 25 so as to maximize their vibration force at a given natural frequency.
A common example of damping is shock absorbers on a vehicle. BW f c Q Where f c resonant frequency Q quality factor. Resonance is witnessed in objects in equilibrium with acting forces and could keep vibrating for a long time under perfect conditions.
We characterize the variance of the additive noise in the observed resonance curve. The Damping Factor A third force damping is at work throughout the speed range. This efficiency to create near-field hot spots can be judged through an LSPR figure-of-merit such as Quality factor Q-factor defined as the ratio of LSPR peak energy to its line width.
In this course you will see how physics can describe these motions mathematically. While the Q factor of an element relates to the losses this links directly in to the bandwidth of a resonator with respect to its. The use of both capacitive and inductive devices in distribution systems leads to resonance phenomena resulting in extremely high or low impedance values.
The Intensity is directly proportional towards the square from the Amplitude and also the line width is inversely proportional towards the Q factor and also the Q factor is really a way of measuring the sharpness of Resonance. Q E stored E lost per cycle. These variations in impedance modify the current and voltage in the distribution system.
This is merely an exercise in algebra. Q factor is such a parameter in Physics which is dimensionless. The free electron density determines the LSPR peak energy while the extent of electron scattering controls the LSPR line width.
The observed resonance curve is the squared magnitude of an observed complex scattering parameter. A high Q resonant circuit has a narrow bandwidth as compared to a low Q. The mathematical representation is.
The goal of Unit 11 of The Physics Classroom Tutorial is to develop an understanding of the nature properties behavior and mathematics of sound and to apply this understanding to the analysis of music and musical instruments. Hence these factors together essentially dictate the. To find the resonant frequency of a single continuous wave we use the.
The quality of Resonance is determined by the Q factor. Q factor or quality factor is a dimensionless parameter that is used to describe the underdamped resonator and characterizes the bandwidth and center frequency of the resonator. Resonant frequency is usually denoted as f 0.
Extended physical systems that have been made to vibrate like a string on a guitar cannot return to their state of equilibrium without exerting forces on the area around them. Recently with the Fano resonance exerting remarkable potential for optical acoustic atomic and electronic applications it is vital to control and even dynamically reconfigure the resonance line shape and bandwidth in addition to its frequency. Q 1 R L C Q 1 R L C.
The Q factor is a dimensionless parameter that indicates the energy losses within a resonant element which could be anything from a mechanical pendulum an element in a mechanical structure or within electronic circuit such as a resonant circuit. It also characterizes a resonators bandwidth relative to its center frequency. If the Q factor goes higher the energy loss goes lower.
Frequency and quality factor especially for resonances that are undercoupled. Resonance An object free to vibrate tends to do so at a specific rate called the objects natural or resonant frequency. Given that the resonance curve is sampled at a fixed number of equally spaced frequencies in the neighborhood of the resonant frequency we determine the optimal frequency spacing in order to minimize the asymptotic standard deviation of the estimate of either or.
This frequency depends on the size shape and composition of the object Such an object will vibrate strongly when it is subjected to vibrations or regular impulses at a frequency equal to or very close to. The reso-nance peak frequency vd and the Q factor Q which allows measurement of dissipation through the sharpness of the resonant peak are the most widely used quantities in these applications. The quality factor relates the maximum or peak energy stored in the circuit the reactance to the energy dissipated the resistance during each cycle of oscillation meaning that it is a ratio of resonant frequency to bandwidth and the higher the circuit Q the smaller the bandwidth Q ƒr BW.

Q Factor What Is It And How Do You Measure It Electrical4u
0 Comments